Introduction
Every year, millions of research papers are published across fields like medicine, engineering, computer science, and social sciences. For students, academics, and professionals, this creates a problem: how do you keep up with all this knowledge? Even if you dedicate hours each day to reading, it’s nearly impossible to digest everything relevant to your work.
Summarizing papers is one solution, but traditional summarization takes time and effort. Enter AI summarization tools — powered by natural language processing (NLP) and large language models (LLMs) — which can condense a 20-page research article into a concise, digestible summary in seconds.
This blog will walk you through why summarizing research papers matters, how AI summarization works, step-by-step workflows, the best tools available, their limitations, and best practices so you can leverage AI responsibly and effectively.
Why Summarizing Research Papers Matters
The challenge of information overload
The sheer volume of new publications is staggering. According to estimates, more than 2.5 million scientific articles are published each year. For a PhD student writing a literature review or a doctor trying to keep up with medical updates, this becomes overwhelming.
Benefits of summarization
- Time savings: Quickly grasp the main findings without reading every word.
- Better comprehension: Summaries simplify jargon, making ideas more approachable.
- Efficient literature reviews: Condense dozens of papers into a few pages of notes.
- Improved collaboration: Share concise insights with peers or colleagues.
A quick scenario
Imagine a master’s student preparing a thesis on climate policy. They need to review 40+ papers in three weeks. Reading every article thoroughly would be impossible. With AI summaries, they can extract key findings, compare methodologies, and identify gaps far more efficiently.
Traditional vs AI-Powered Summarization

Traditional methods
- Skimming abstracts and conclusions
- Highlighting key sections
- Annotating PDFs
- Writing manual notes
While effective, these methods are time-consuming and often depend on the reader’s subject knowledge. Important nuances can easily be missed.
AI-powered methods
AI summarization tools use machine learning, NLP, and LLMs to scan full research papers and generate concise versions. They can highlight:
- Key findings
- Methodologies
- Limitations
- Future directions
Advantages:
- Speed (seconds vs hours)
- Scalability (summarize dozens of papers in bulk)
- Flexibility (choose bullet points, abstracts, or narrative summaries)
How AI Summarization Tools Work
AI summarization relies on two main approaches:
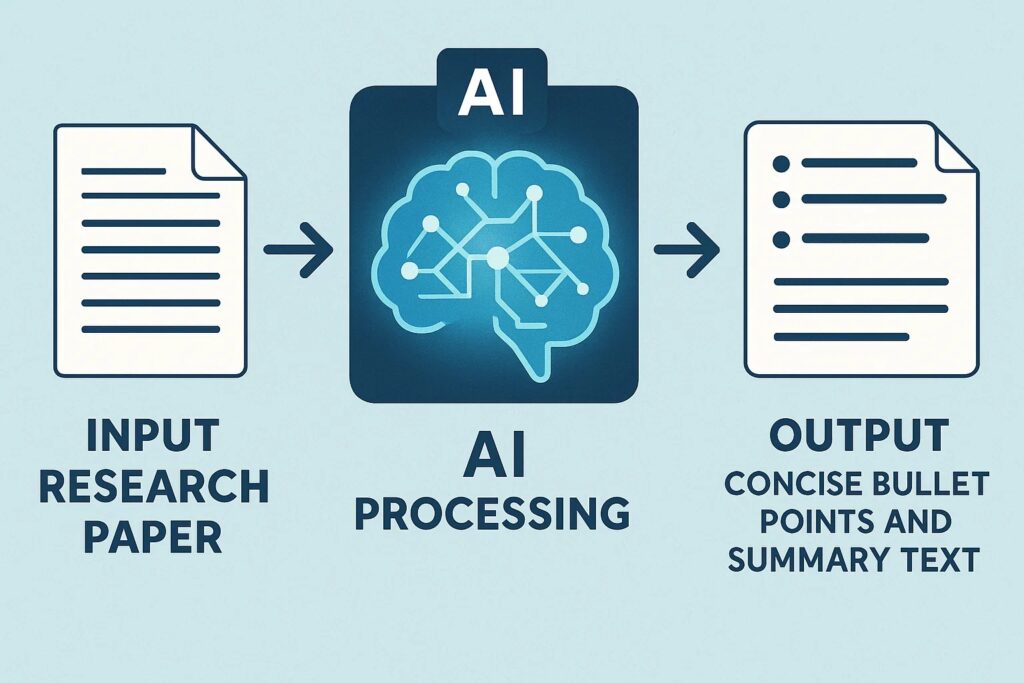
Extractive Summarization
The AI selects the most important sentences directly from the text. Think of it like a smart highlighter. While accurate, it may lack flow.
Abstractive Summarization
Here, the AI rephrases and condenses information, creating new sentences that capture meaning. This mimics how humans summarize.
Handling academic language
Modern tools are trained on large text corpora, enabling them to handle technical jargon, citations, and structured formats. Some tools even recognize sections like Methods, Results, and Discussion, tailoring summaries accordingly.
Example:
Original: “Our double-blind, randomized trial with 300 participants demonstrated a statistically significant 12% reduction in blood pressure over 12 weeks.”
- Extractive summary: “Double-blind, randomized trial with 300 participants… 12% reduction in blood pressure.”
- Abstractive summary: “The study found that a randomized clinical trial reduced blood pressure by 12% over three months.”
Step-by-Step Guide: Summarizing a Research Paper with AI
Let’s break down how to use AI to summarize papers effectively:
1. Choose the right tool
Different tools have different strengths (more on this later). Some handle PDFs, others need plain text or DOIs.
2. Upload or input the paper
Most tools let you paste text, upload a PDF, or enter a DOI/URL.
3. Select the summarization style
Options may include:
- Bullet points
- Key findings only
- Abstract-style summary
- Methodology + results breakdown
4. Generate the initial summary
Hit “summarize” and let the AI process the document.
5. Evaluate accuracy
Compare the AI summary with the paper’s abstract and conclusion. This ensures it captured the essence.
6. Refine output
Use prompts like:
- “Summarize in 5 bullet points highlighting methodology, results, and limitations.”
- “Explain this paper for a non-expert.”
7. Cross-check terminology
Ensure technical terms, statistics, and citations weren’t distorted.
8. Store and organize
Export summaries into a knowledge management tool (e.g., Notion, Obsidian, Mendeley).
💡 Pro tip: Always combine AI summaries with your own notes for deeper understanding.
Best AI Tools for Summarizing Research Papers
Here are some of the most effective tools available today:
1. ChatGPT / GPT-4
- Strengths: Flexible prompts, supports bullet points, abstracts, layman explanations.
- Weaknesses: Needs careful prompting; may hallucinate details if not grounded in the text.
- Best for: Custom, conversational summarization.
2. Elicit.org
- Strengths: Research-focused, builds literature reviews, extracts methods/results.
- Weaknesses: Limited to certain databases.
- Best for: Academic workflows, systematic reviews.
3. Scholarcy
- Strengths: Direct PDF summarization, highlights key sections, auto-references.
- Weaknesses: Paid features needed for bulk processing.
- Best for: Quick, structured summaries of full papers.
4. QuillBot Summarizer
- Strengths: Easy-to-use, paraphrasing + summarization.
- Weaknesses: Less specialized for academic language.
- Best for: General summaries, study notes.
5. Scispace (formerly Typeset)
- Strengths: AI copilot for research papers, explains jargon, integrates with PDFs.
- Weaknesses: Still evolving.
- Best for: Students new to complex academic texts.
6. Iris.ai
- Strengths: Semantic search, context-based summarization, research discovery.
- Weaknesses: Requires setup and training for best results.
- Best for: Advanced researchers.
7. Consensus
- Strengths: Focuses on evidence-based summaries, finds consensus across multiple papers.
- Weaknesses: Limited scope.
- Best for: Policy, medical, and evidence-driven fields.
8. Paper Digest
- Strengths: Instant academic paper summaries, supports bulk.
- Weaknesses: Sometimes oversimplifies.
- Best for: Quick overviews of many papers.
Comparison Table
| Tool | Input Type | Output Style | Accuracy | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | Text, PDF | Flexible | High (with prompts) | Custom summaries |
| Elicit.org | DOI/Text | Structured | High | Systematic reviews |
| Scholarcy | Highlights, Key Points | High | Students, academics | |
| QuillBot | Text | Shortened/Paraphrased | Medium | Study notes |
| Scispace | PDF/Text | Jargon explained | High | Beginners |
| Iris.ai | PDF/Text | Semantic Summaries | High | Researchers |
| Consensus | Text/Search | Evidence-Based | Medium-High | Medical/policy |
| Paper Digest | Instant Highlights | Medium | Quick overviews |
Limitations & Risks of AI Summarization
Despite the benefits, AI is not perfect.
- Loss of nuance: Subtle findings or methodological caveats may be missed.
- Over-simplification: Important context could be stripped away.
- Misinterpretation: AI may confuse technical terms.
- Hallucination: Sometimes invents details not in the paper.
- Academic integrity: Copying summaries directly can border on plagiarism.
Best Practices for Using AI Summaries
- Cross-check: Always verify summaries against the original.
- Use as a starting point: Treat AI output as an aid, not a final source.
- Combine with human notes: Add your interpretations.
- Stay ethical: Cite original papers, not the AI summary.
- Recommended workflow:
- Read the abstract.
- Generate AI summary.
- Skim methods & results.
- Verify.
Future of AI in Academic Summarization
The next generation of AI tools will likely:

- Summarize multimodal content (figures, graphs, tables).
- Integrate directly with reference managers (Zotero, Mendeley).
- Provide personalized summaries based on your research focus.
- Act as research assistants, suggesting related studies and generating draft literature reviews.
This could fundamentally reshape how knowledge is consumed in academia.
Conclusion
Summarizing research papers is essential for managing today’s flood of academic literature. While traditional methods work, they’re slow and limited. AI tools — from ChatGPT to Scholarcy and Elicit — offer fast, flexible, and accurate summaries that save time and support better research workflows.
Still, AI should not replace human judgment. The best approach is to combine AI summarization with critical reading and verification. Used wisely, these tools can turn information overload into manageable, actionable knowledge.
👉 Ready to try it? Pick one or two tools from this guide, upload a paper, and see how AI can transform your research process.
FAQs
Can AI replace reading research papers?
No. AI can speed up comprehension, but detailed understanding requires reading key sections like Methods and Results.
Are AI summaries reliable for academic writing?
They’re reliable for overviews, but not accurate enough to cite without verification. Always cross-check with the original.
What’s the best free tool?
ChatGPT (with free access) and Elicit.org are strong free options. For PDFs, Scholarcy’s free version works well.