The internet has made the world smaller, but language is still one of the biggest barriers to global communication. If your business only creates content in one language, you’re missing out on millions of potential readers, customers, and opportunities. In fact, research shows that 65% of consumers prefer content in their native language, and over 40% won’t buy products from websites that aren’t localized.
Until recently, translating content into multiple languages was expensive, slow, and difficult. Brands relied on professional translators or agencies, which meant scaling content across 10, 20, or even 50 languages was out of reach for most companies.
Enter AI-powered translation. Advances in machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) have made it possible to translate content faster, cheaper, and with increasing accuracy. From blog articles and product descriptions to marketing campaigns and customer support, AI can handle much of the heavy lifting — but there are best practices you need to follow to ensure accuracy, cultural relevance, and SEO optimization.
In this guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to know about translating content using AI: how it works, its benefits and limitations, step-by-step processes, and practical tips to get the best results.
Why Translate Content?
Before diving into AI, let’s answer the bigger question: why should you translate your content at all?
1. Global Reach
The internet audience is diverse and multilingual. Translating content allows you to connect with users across borders, opening doors to new markets without needing to relocate or heavily invest in local offices.
2. Better User Experience
People are more likely to engage with, trust, and buy from brands that speak their language. A simple product description or blog post in a reader’s native tongue can build credibility and loyalty.
3. SEO Benefits
Search engines like Google index content differently in each language. By translating and optimizing content for local keywords, you can rank in new markets and gain organic traffic that competitors might overlook.
4. Compliance & Inclusivity
In industries like healthcare, finance, or education, accurate translations can be a regulatory requirement. Beyond compliance, translating content ensures inclusivity and accessibility.
Example: A SaaS company might translate its support documentation into Spanish, French, and Mandarin, reducing customer service tickets and improving adoption in those regions.
Traditional Translation vs. AI Translation
For decades, businesses relied on human translators or agencies to localize content. Let’s compare that with AI-driven methods.
Traditional Translation
- Pros:
- High accuracy in nuance and cultural context
- Human touch ensures tone and style are preserved
- Cons:
- Time-consuming — translating a 2,000-word article could take days
- Expensive — costs scale linearly with word count and number of languages
- Difficult to scale across dozens of languages simultaneously
AI Translation
- Pros:
- Speed: translate entire websites or documents in minutes
- Cost-effective: many tools charge per word or offer unlimited translations
- Scalable: translate into 50+ languages at once
- Cons:
- May miss cultural nuance, idioms, or industry-specific jargon
- Risk of awkward phrasing or tone mismatch
- Accuracy depends on the quality of the tool and language pair
The Hybrid Approach
The best practice today isn’t to choose one over the other — it’s to combine AI with human review. AI handles the heavy lifting, while human editors polish the translation for accuracy and context.
How AI Translation Works
AI translation has evolved far beyond word-for-word substitutions.

Neural Machine Translation (NMT)
Tools like Google Translate and DeepL use neural networks to analyze context, syntax, and semantics, producing translations that are more natural than earlier rule-based systems.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Models like ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini go a step further, generating translations that adapt tone and context. Instead of just translating, they can rephrase content for fluency, readability, and brand voice.
Training Data
AI models are trained on massive bilingual and multilingual datasets. They learn from millions of examples to predict the most accurate translation in context.
Post-Editing
AI outputs are typically not final. Human editors (or at least a quality check process) are needed to correct errors, adapt idioms, and ensure cultural fit.
Best Practices for Translating Content Using AI
This is the heart of the process — the strategies that make the difference between sloppy machine translations and professional-grade localized content.

1. Define Goals & Target Audience
- Identify which markets and languages matter most.
- Example: Spanish in Spain differs from Spanish in Mexico or Argentina. Tailor your translations accordingly.
2. Choose the Right AI Tool
Not all tools are created equal. Some prioritize accuracy, others scalability.
- DeepL → known for contextual accuracy in European languages
- Google Translate → broad coverage of 100+ languages
- ChatGPT / LLMs → versatile, customizable, able to adapt tone
- Lokalise, Weglot, Smartling → designed for businesses integrating translations into workflows
3. Ensure Cultural & Contextual Accuracy
- Avoid literal translations for idioms or slang.
- Adjust measurements, currencies, and date formats.
- Example: An American “Black Friday Sale” may need a different framing in other regions where the holiday doesn’t exist.
4. Optimize for Multilingual SEO
- Use keyword research tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush for localized keywords.
- Don’t just translate keywords directly — identify what locals actually search for.
- Add hreflang tags to signal search engines about language versions.
5. Maintain Formatting & Tone Consistency
- Keep brand voice consistent across all translations.
- Adjust for text expansion — some languages (like German) take up more space.
- Ensure headings, CTAs, and buttons remain clear and action-oriented.
6. Quality Assurance & Post-Editing
- Always proofread AI outputs.
- Use a translation glossary (brand terms, product names, slogans) to maintain consistency.
- Involve native speakers for final review whenever possible.
7. Legal & Compliance Considerations
- For regulated industries (finance, law, healthcare), mistranslations can cause liability issues.
- Ensure disclaimers, contracts, and compliance documents are professionally validated.
Step-by-Step Guide: Translating Content Using AI
Here’s a practical workflow you can follow:
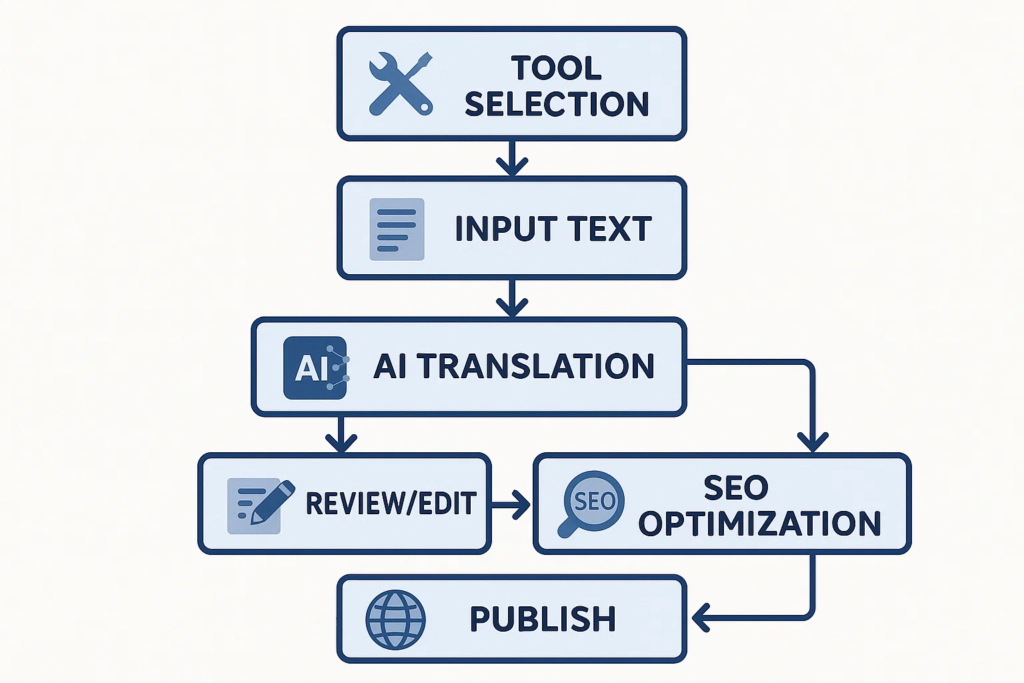
- Select Your AI Tool – Choose based on language needs and budget.
- Upload or Input Content – Paste text or connect via API for large-scale projects.
- Run Translation – Generate translations for chosen languages.
- Review Output – Spot-check for major tone or context errors.
- Apply SEO Adjustments – Add localized keywords, meta descriptions, and tags.
- Conduct Quality Check – Use back-translation or human editors.
- Publish & Test – Launch content, monitor engagement, and A/B test.
- Iterate with Feedback – Collect user input from native speakers to refine.
Tip: Many businesses use AI for the first draft, then send the output to freelance editors on platforms like Upwork or Fiverr for polishing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-relying on AI: Never publish raw AI translations without review.
- Ignoring cultural nuances: What works in one market may confuse or offend in another.
- Skipping SEO localization: Translations without localized keywords won’t rank.
- One-size-fits-all translations: Spanish in Spain ≠ Spanish in Latin America.
- Not updating translations: Language evolves — outdated translations can hurt credibility.
Case Studies & Real-World Examples
Case 1: E-Commerce Brand
A global retailer used AI to translate 20,000+ product descriptions into French and German. With human editors reviewing 10%, they reduced costs by 70% while improving sales in new regions.
Case 2: SaaS Company
A SaaS platform integrated AI translation for support articles. By translating documentation into Spanish and Japanese, they cut support tickets by 30%.
Case 3: AI Translation Fail
A brand once launched a slogan that AI mistranslated into a phrase with unintended offensive meaning in Chinese. The lesson: always double-check sensitive content.
The Future of AI in Translation

The future looks promising:
- Contextual understanding: AI is getting better at capturing nuance.
- Customization: Brands can train AI on their own tone, style, and glossary.
- Real-time translation: AI will soon make live multilingual interactions seamless (think Zoom meetings with instant subtitles).
But even with improvements, the human touch will remain essential for accuracy, empathy, and cultural sensitivity.
Conclusion
AI has transformed the way we think about translation. It enables businesses to scale content globally, cut costs, and move faster than ever before. But the best results come when AI and humans work together — machines for speed and scale, humans for context and nuance.
If you’re looking to explore the best tools to start translating your content, check out the curated AI translation solutions at AIToolBank — where you can compare features, pricing, and user reviews to find the right fit for your business.
FAQs
Is AI translation accurate?
It’s highly accurate for general content but should always be reviewed for nuance and industry-specific terms.
Which AI tool is best for translation?
DeepL for accuracy, Google Translate for coverage, and ChatGPT for customizable, tone-aware translations.
Can AI handle SEO translations?
AI can generate translations, but you need human research for localized keywords.
Should I replace human translators with AI?
Not entirely. AI is best for drafts and bulk content, while humans refine and validate.
How do I avoid mistakes with AI translation?
Always review, use glossaries, and involve native speakers for sensitive or legal content.